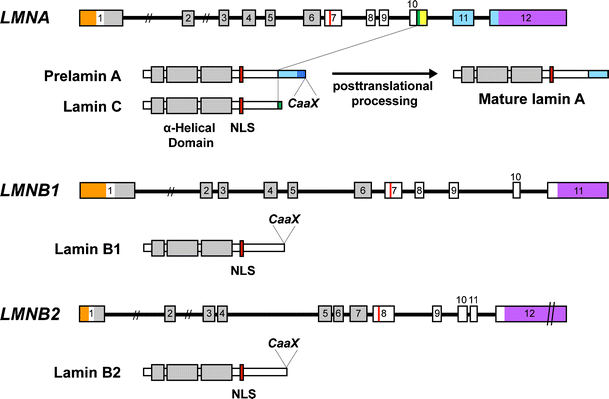
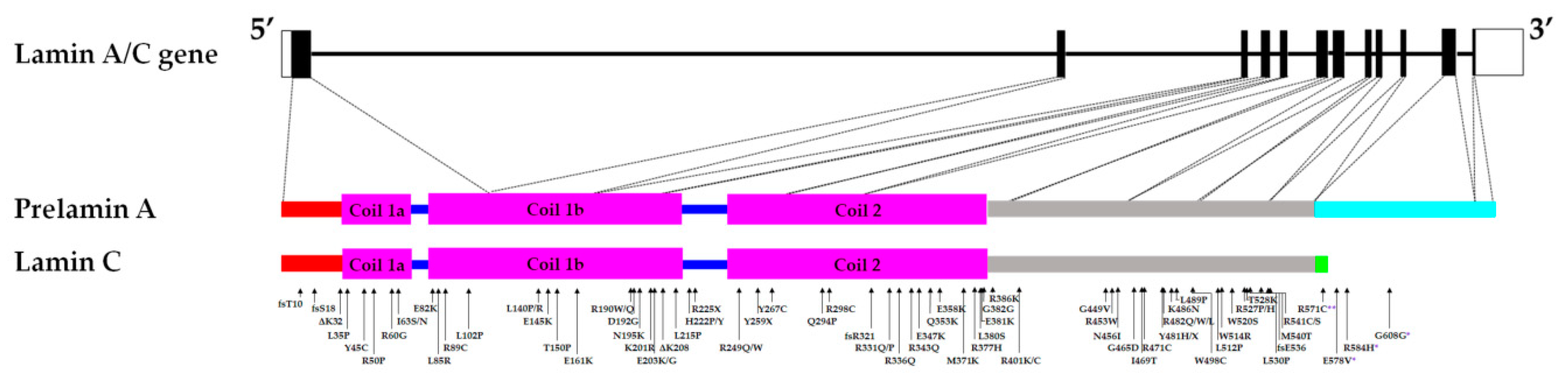
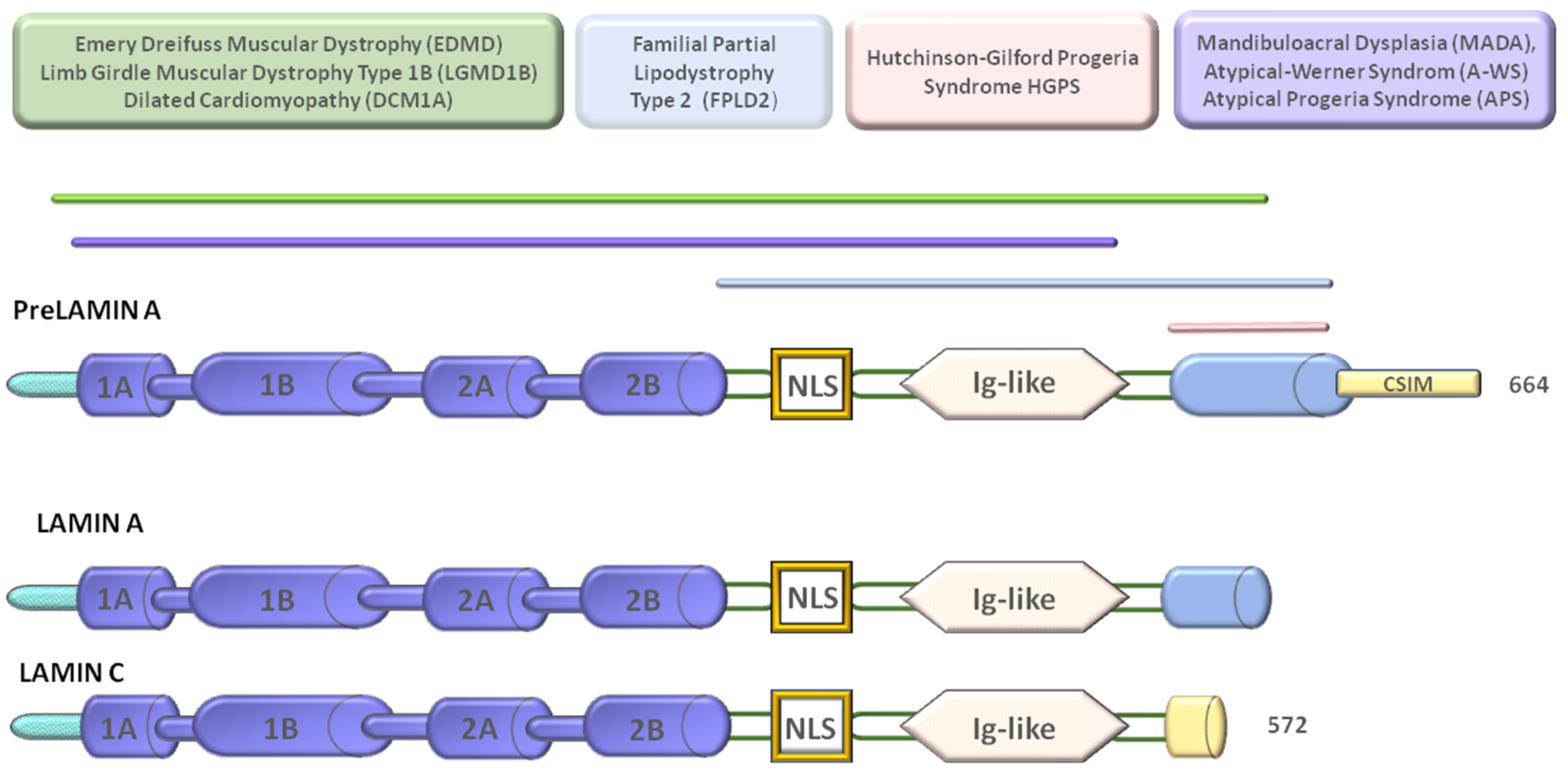
Nuclear Lamins And Laminopathies

Developmental and tissue specific variation of the lamins and nuclear envelope protein expression.
Nuclear lamins and laminopathies. The physical functions of the lamins. The nuclear periphery and chromatin organization. To read the full text of this research you can request a copy directly from the author. Nuclear lamins and laminopathies.
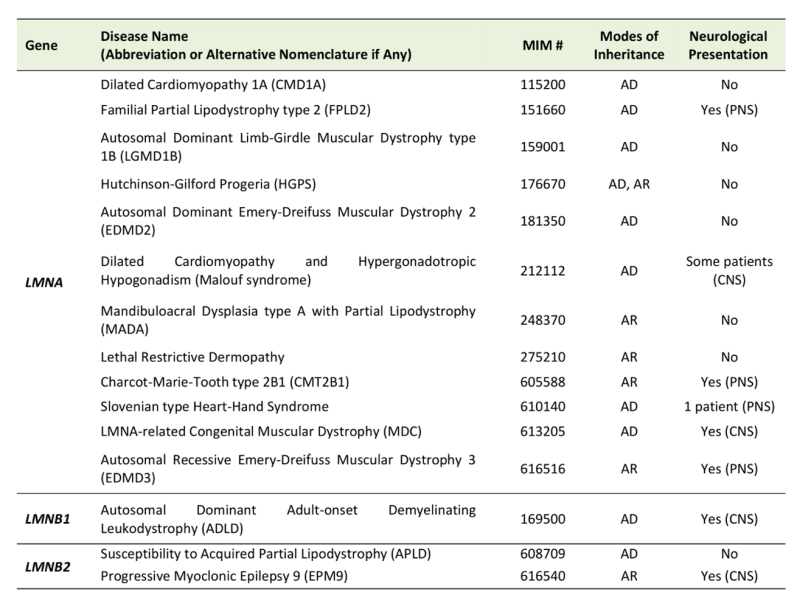
Luxton et al 2011. Laminopathies and their role in premature ageing j. Mutations in genes encoding nuclear lamins particularly lmna encoding the a type lamins cause a range of phenotypically diverse diseases. The phenotypes and genetic abnormalities of these disorders have been extensively described.
Concluding remarks and relevance to contemporary. Ramaekers and gis e le bonne and r. Laminopathies and their role in premature ageing author jos l v broers and frans c. The contrasting expression patterns of a type and b type lamins together with the finding that b type lamins are essential for cell survival have given rise to the notion that b type lamins are the fundamental building blocks of the nuclear lamina while a type lamins have more specialized functions.
Loss of either type of lamin impairs nucleo cytoskeletal coupling. J cell biol 151 1155 1168 pubmed crossref google scholar. Hale et al 2008. The laminopathies and nuclear envelopathies.
Folker et al 2011. Different pathways of assembly during nuclear envelope formation in living cells. Ben yaou and c. Lammerding et al 2004.
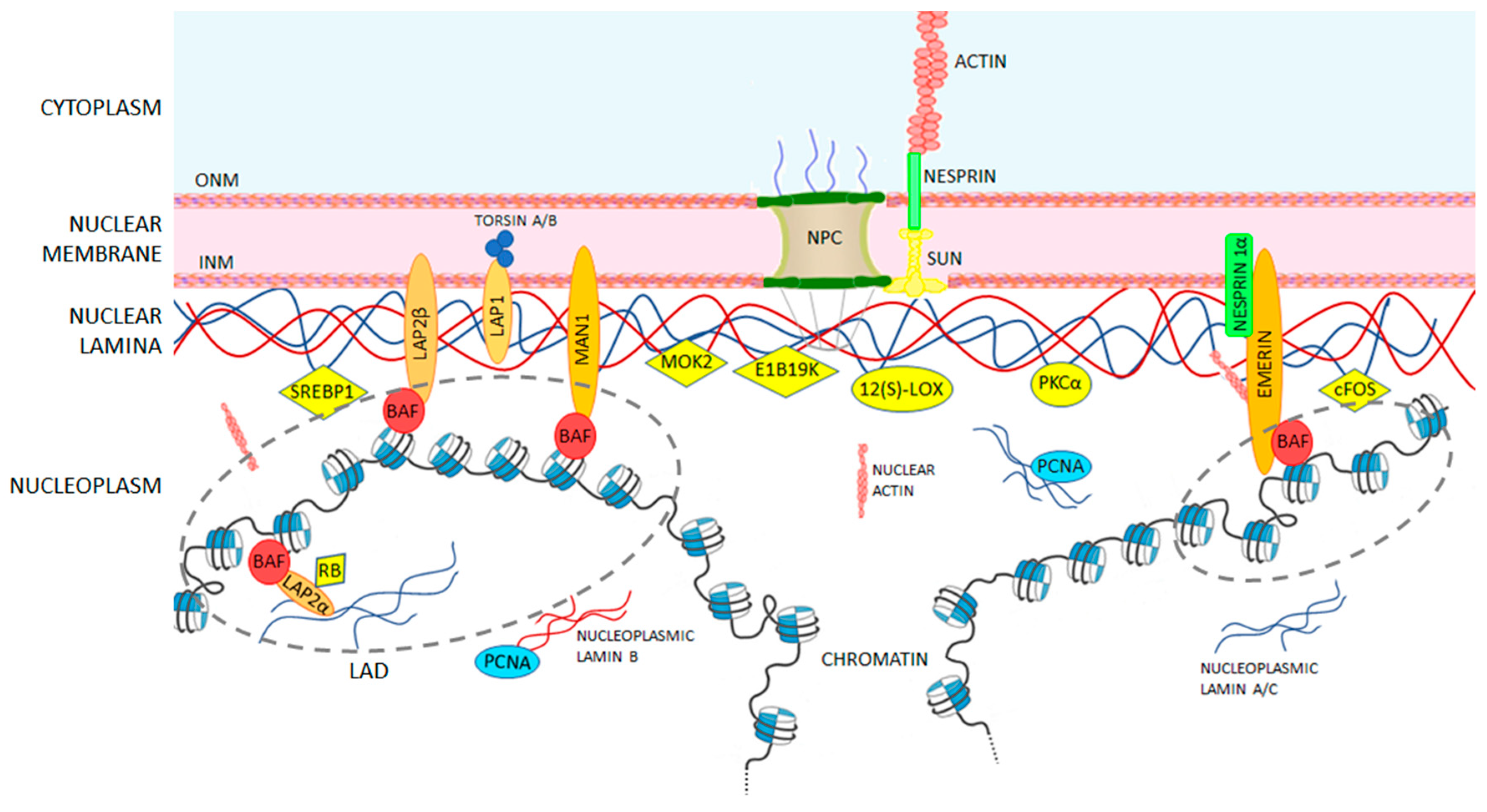
Nico stuurman susanne heins ueli aebi 1998. It has been demonstrated that nuclear lamins are important proteins in maintaining cellular as well as nuclear integrity and in maintaining chromatin organization in the nucleus. Journal of structural biology 122 42 46. Their structure assembly and interactions.
Nuclear lamins and signaling. Moir rd yoon m khuon s et al 2000 nuclear lamins a and b1. Ben yaou and. Cells that lack a type lamins have defects in nuclear positioning and disturbed cytoskeletal organization with reduced stiffness broers et al 2004.
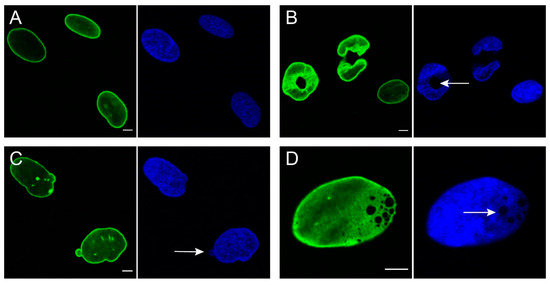
While mutations causing laminopathies have been shown to produce abnormalities in nuclear morphology how these disease causing mutations or resultant alterations in nuclear structure lead to pathology is only starting to be understood.