Nuclear Lamin B1
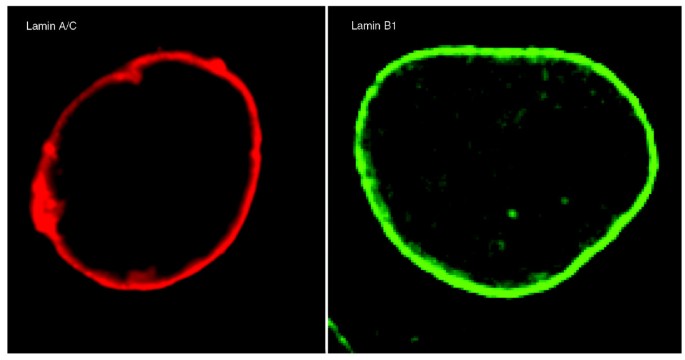
The cells were fixed with 100 methanol 5 min and then permeabilized with 0 1 pbs tween for 20 min.
Nuclear lamin b1. Here we investigated the contribution of major lamin subtypes lamins a c and b1 to nuclear mechanics by analyzing nuclear shape nuclear dynamics over time nuclear deformations under strain and cell viability under prolonged mechanical stimulation in cells lacking both lamins a and c cells lacking only lamin a i e. The nuclear lamina consists of a two dimensional matrix of proteins located next to the inner nuclear membrane. The nuclear lamina consists of two components lamins and nuclear lamin associated membrane proteins. The lamin family of proteins make up the matrix and are highly conserved in evolution.
Nuclear lamin isoforms assemble into fibrous meshworks within the nuclear lamina nl where they are associated with nuclear pore complexes npcs. The nuclear envelope is composed of two membranes. When using lamin b1 antibodies as nuclear loading controls be aware that in apoptotic cells lamin b1 is cleaved kottke tj et al. Lamin structure and assembly.
Specifically this protein is located in the nuclear lamina a mesh like layer of intermediate filaments and other proteins that is attached to the inner membrane of the nuclear envelope. The outer nuclear membrane onm which faces the cytoplasm and the inner nuclear membrane inm which faces the inside of the. Furukawa et al 1994. Lamin b1 and lamin b antibodies are extremely useful as nuclear loading controls for use with nuclear extracts.
Lamin b1 will also be removed from a nuclear prep if the nuclear membranes are spun out. A type lamins are encoded by a single gene lmna. Lamin b1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the lmnb1 gene. B type lamins are ubiquitously expressed from the genes lmnb1 and lmnb2 to form the two main isoforms lamin b1 and b2.
Although the lamins and npcs are major components of the nuclear envelope ne little is known about their structural relationships. Introduction the nuclear envelope separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm. The nuclear lamina is composed mainly of type v intermediate filament proteins termed lamins which are classified into a and b type. Lamins are grouped into a type and b type lamins.
We used 3d structured illumination microscopy 3d sim and sub pixel image analysis to show that npcs are closely. A type lamins are mainly expressed in differentiated cells from the lmna gene that undergoes alternative splicing to form lamin a and lamin c. Lamin b1 is a scaffolding supporting component of the nuclear envelope which is the structure that surrounds the nucleus in cells. The lamins are type v intermediate filaments which can be categorized as either a type lamin a c or b type lamin b 1 b 2 according to homology of their dna sequences biochemical properties and cellular localization during the cell cycle.