Nuclear Actin Lamin
B type lamins are ubiquitously expressed from the genes lmnb1 and lmnb2 to form the two main isoforms lamin b1 and b2.
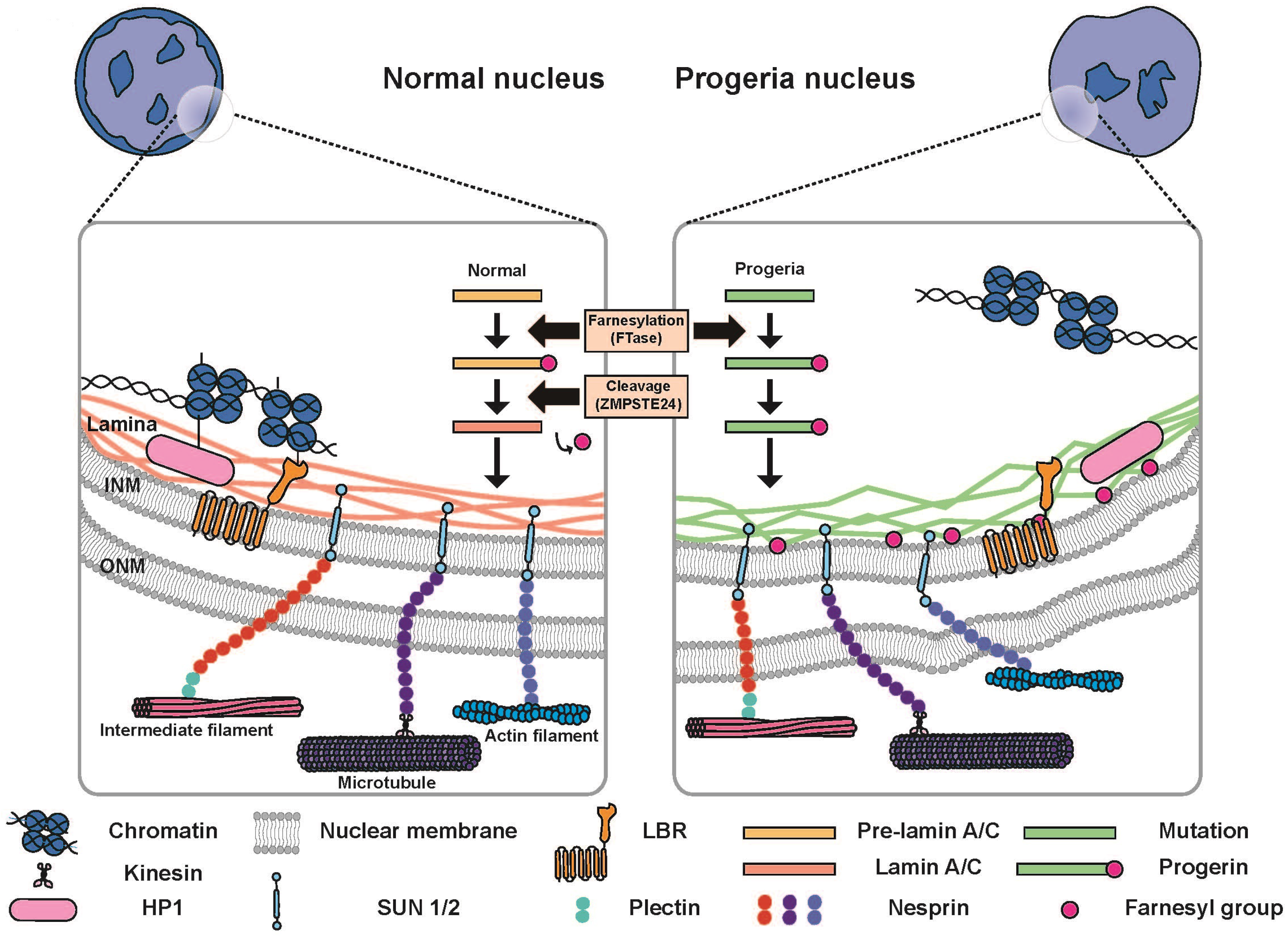
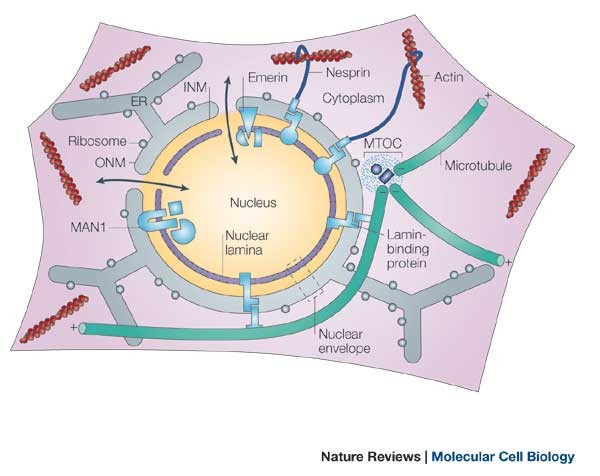
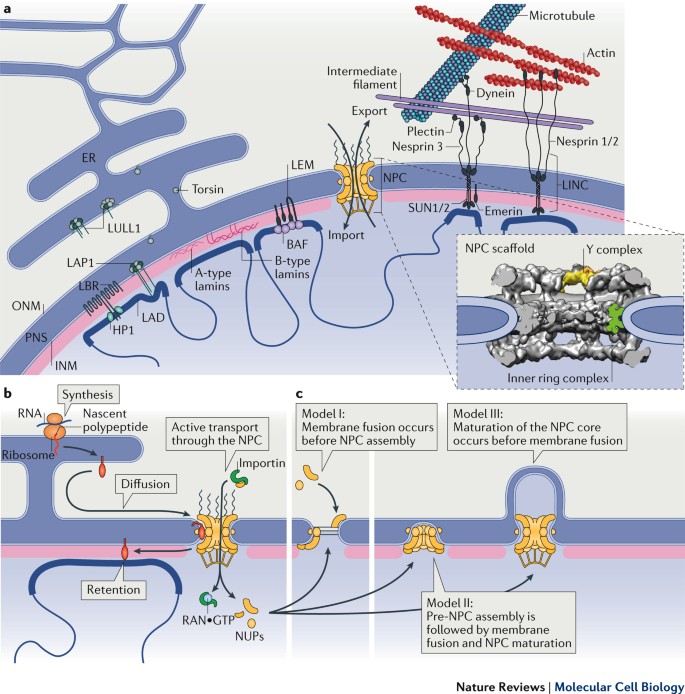
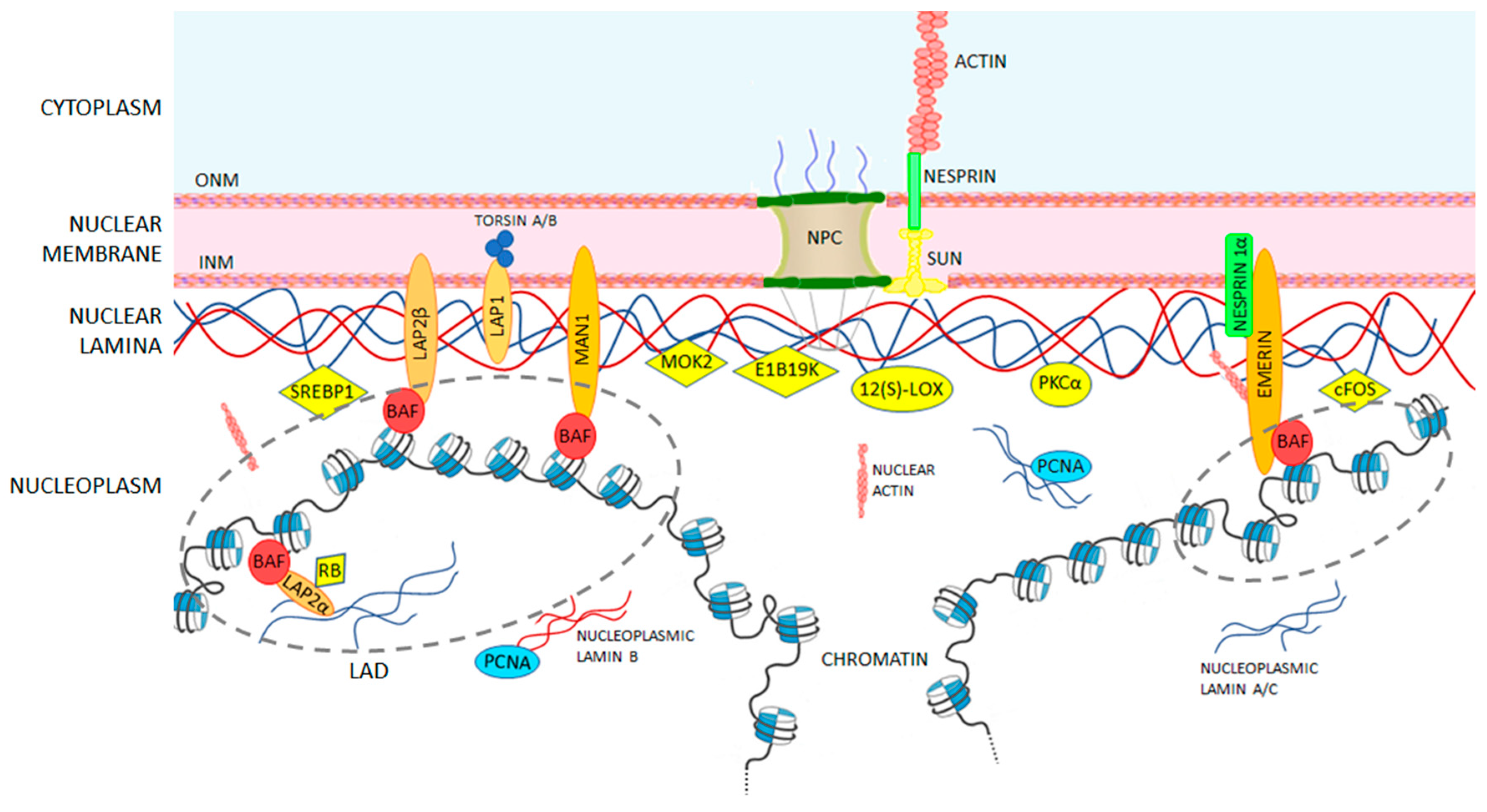
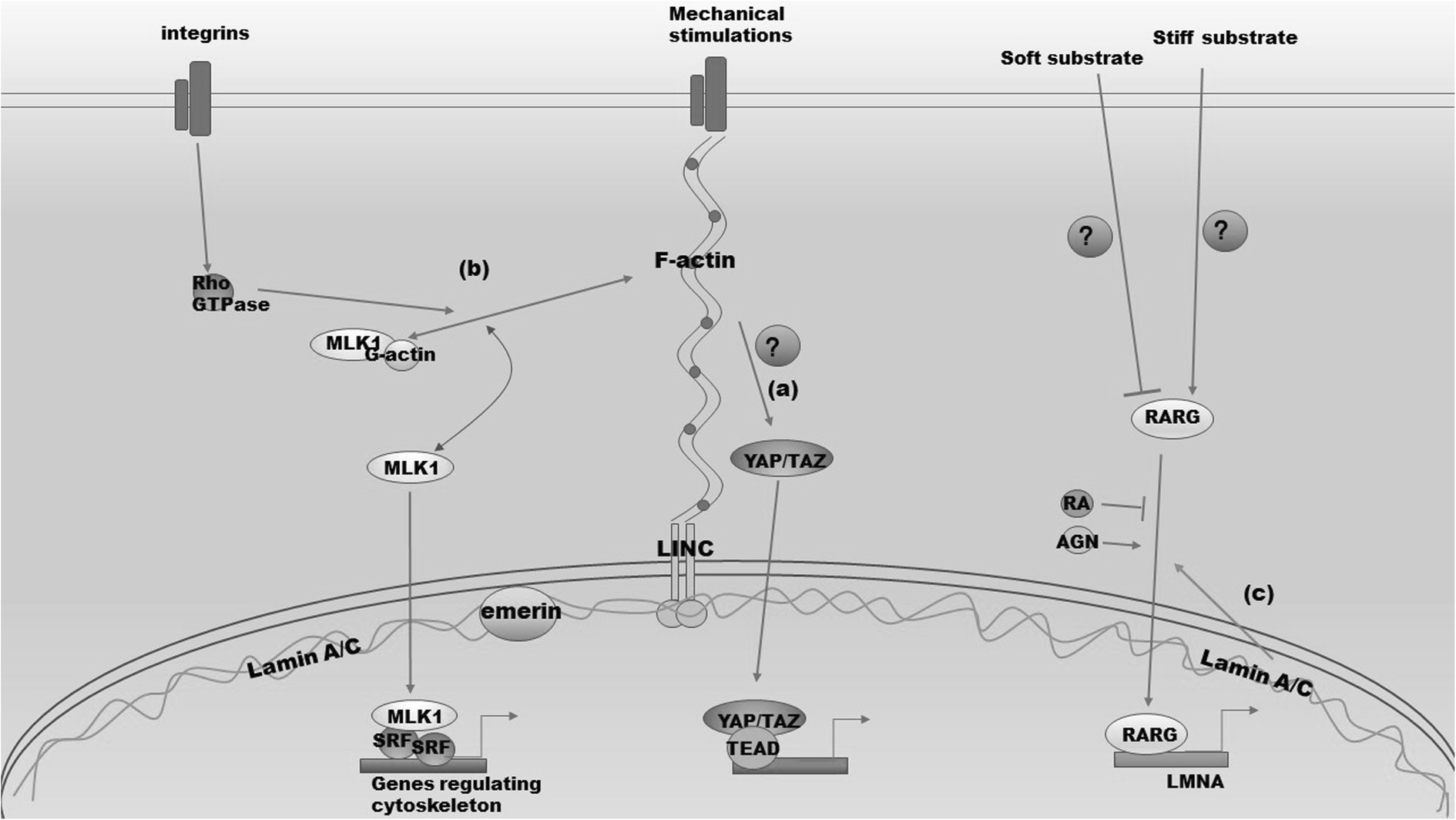
Nuclear actin lamin. The 2014 current biology paper reported the presence of radially oriented actin bundles or spikes growing out of a lamin associated actin network and into the nuclear envelope. The nuclear lamina is composed mainly of type v intermediate filament proteins termed lamins which are classified into a and b type. The nuclear lamina is highly important for migration of both primary and cancer cells. The nuclear lamina consists of two components lamins and nuclear lamin associated membrane proteins.
A type lamins are mainly expressed in differentiated cells from the lmna gene that undergoes alternative splicing to form lamin a and lamin c. Perhaps lamin and actin interact in the nucleus. Nuclear actin in the assembly and transport of viral capsids. The lamins are type v intermediate filaments which can be categorized as either a type lamin a c or b type lamin b 1 b 2 according to homology of their dna sequences biochemical properties and cellular localization during the cell cycle.
The finding that syne anc 1 or whatever name s the workers in this field finally decide upon contain lamin and actin binding domains raises the interesting possibility that these proteins serve to link the inner nuclear membrane the lamins comprising the lamina and nuclear. Three members of the alphaherpesvirinae subfamily herpes simplex virus 1 hsv 1 herpes simplex virus 2 hsv 2 and pseudorabies virus prv were shown to induce filament formation in the nuclei of infected cells 48 49 in the case of prv infection the observed filaments had an average length of 3 µm and a diameter of. B type lamins are important for proper migration of epicardial cells and neurons and increased lamin b to lamin a ratio accelerates cancer cell migration through confined spaces.