Non Binding Price Floor Definition

A price floor must be higher than the equilibrium price in order to be effective.
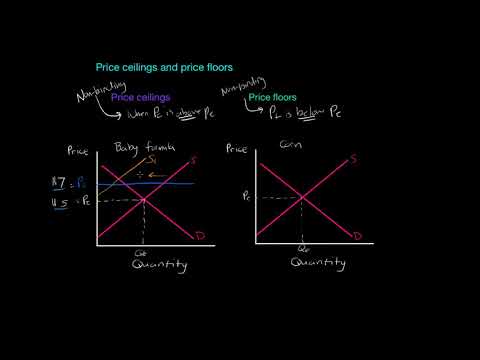
Non binding price floor definition. If the price floor is above the equilibrium price. The equilibrium market price is p and the equilibrium market quantity is q. If the price floor is under the equilibrium price. This is an example of a non binding or not effective price ceiling.
This is a price floor that is less than the current market price. A price ceiling is a government or group imposed price control or limit on how high a price is charged for a product commodity or service governments use price ceilings to protect consumers from conditions that could make commodities prohibitively expensive. Another way to think about this is to start at a price of 0 and go up until you the price ceiling price or the equilibrium price. Note that the price ceiling is above the equilibrium price so that anything price below the ceiling is feasible.
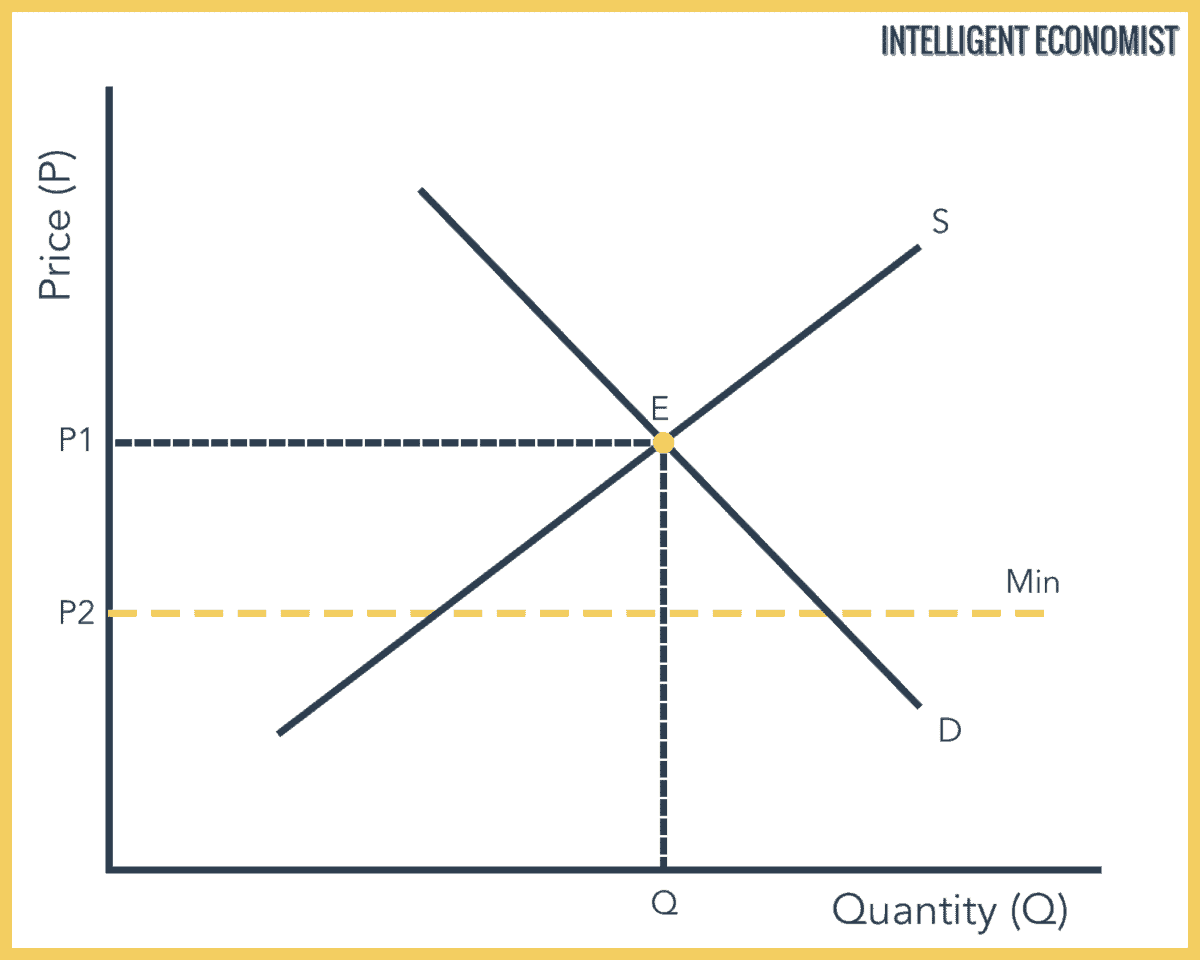
There are two types of price floors. At the price p the consumers demand for the commodity equals the producers supply of the commodity. A price floor is a government or group imposed price control or limit on how low a price can be charged for a product good commodity or service. Such conditions can occur during periods of high inflation in the event of an investment bubble or in the event of monopoly.
Binding vs non binding price floor. Economics classes want students to be able to recognize the difference between binding and non binding price floors. The trick is to remember that prices are free to operate above a price floor just like standing on a floor so any market price above the price floor will not be affected in any way. A legal minimum on the price of a good binding.
A price floor is a form of price control another form of price control is a price ceiling. The price floor is no binding i e it doe snot distort the market outcome if it is set at a level below the market. If price ceiling is above the equilibrium price. A price floor or minimum price is a lower limit placed by a government or regulatory authority on the price per unit of a commodity.
This video explains and shows how a non binding price floor becomes ineffective. A non binding price floor is one that is lower than the equilibrium market price. The equilibrium price commonly called the market price is the price where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external. Consider the figure below.